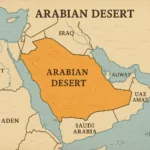
Location & Continent
Continent: Asia
Countries: Saudi Arabia, Oman, Yemen, United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Iraq, Qatar, Kuwait
Coordinates: 22°N, 45°E
Click to load the interactive map
Photos of the Arabian Desert
Physical Features
Area: ~2.330.000 km² (fifth largest desert in the world)
Length: About 2,300 km
Width: About 1,100 km
Elevation: Generally 300–1,000 m; Jebel Shammar mountains exceed 1,800 m
Climate & Precipitation
Temperature: Summer highs often exceed 45–50°C; winter nights can drop below 0°C
Precipitation: Less than 100 mm annually; some regions under 30 mm
Ecological Features
Ecozone: Palearctic desert belt
Biome: Deserts and xeric shrublands
Ecoregions: Arabian Desert and East Saharo-Arabian Xeric Shrublands, Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter)
Flora & Fauna
Flora: Date palms in oases, saltbush, acacias, tamarisk, desert grasses
Fauna: Arabian oryx, sand gazelles, fennec foxes, jerboas, vipers, desert monitors, and migratory birds
Geology & Notable Features
Geology: Sand seas (ergs), gravel plains, salt flats, volcanic fields, rocky plateaus
Notable Features: Rub’ al Khali (Empty Quarter), An Nafud Desert, Dahna Desert, Harrat volcanic fields
Introduction
The Arabian Desert is one of the world’s largest deserts, covering an area of approximately ~2.330.000 km². Distinguished by its unique ecosystems, mesmerizing landscapes, and rich cultural heritage, the Arabian Desert is situated on the Arabian Peninsula. This vast expanse is not only a product of nature’s fascinating transformations but also serves as a backdrop to numerous ancient civilizations.
Geography of the Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert is bordered by the Persian Gulf to the northeast, the Red Sea to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south. This desert encompasses several countries, including Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Oman, United Arab Emirates, and parts of Yemen and Iraq. The geographical features include:
- Sand Dunes: The Rub’ al Khali, or Empty Quarter, is the largest continuous sand desert in the world.
- Mountain Ranges: The Hijaz Mountains stretch along the western region, presenting a striking contrast to the plains and dunes.
- Coastal Areas: The desert region also includes coastal plains along the Gulf of Aqaba and the Red Sea.
The climate is predominantly characterized by extreme temperatures, with summer highs reaching up to 50°C (122°F).
Climate and Weather Patterns
The climate of the Arabian Desert can be classified as bitterly hot in summer and mild to cool in winter. Rainfall is scarce, averaging 3 to 5 inches annually. However, the occurrence of seasonal rains can lead to occasional desert blooms, creating a stark contrast against the arid landscape. Some key features include:
- High UV Index: The UV radiation levels can be dangerously high, urging residents to seek shade.
- Wind Patterns: Strong winds often lead to dust storms, reducing visibility drastically and impacting travel.
Flora and Fauna
Despite its harsh conditions, the Arabian Desert is home to a remarkable variety of flora and fauna. Adaptations such as drought resistance and nocturnal habits allow these plants and animals to thrive.
| Species | Type | Habitat |
|---|---|---|
| Date Palm | Plant | Oasis |
| Arabian Oryx | Mammal | Grasslands |
| Sand Gazelle | Mammal | Sand Dunes |
| Desert Fox | Mammal | Desert |
This table illustrates some of the remarkable species found in this arid environment.
Cultural Significance
The Arabian Desert is not just a remarkable geographical feature; it is also a cradle of rich cultural heritage. The Bedouins, traditionally nomadic tribes, have adapted to the desert’s challenging environment and maintain a lifestyle that resonates with its history. Elements of culture in the Arabian Desert include:
- Architecture: Traditional tents, known as “bayt al-sha’ar,” crafted from goat hair, are emblematic of Bedouin life.
- Literature: The desert has inspired countless poets, authors, and artists through the ages, celebrating its mystique and beauty.
- Trade Routes: Historically, trade routes such as the Incense Route traversed the desert, facilitating cultural exchanges and economic prosperity.
Tourism and Exploration
Today, the Arabian Desert attracts tourists seeking adventure, exploration, and cultural experiences. Popular activities include:
- Sand Dune Bashing: Adventurous off-road driving on the desert dunes.
- Camel Safaris: Traditional camel rides offer a fascinating glimpse into Bedouin culture.
- Desert Camping: Stargazing amidst the vast arid landscape provides a magical experience.
With modern amenities and guided tours, visitors can explore the rich landscapes while ensuring safety and comfort.
Conclusion
In summary, the Arabian Desert is a unique environment characterized by its vastness, severe climate, and ecological diversity. It serves as a vital geographical and cultural landmark, inviting exploration and contemplation. This desert not only offers a glimpse into the natural world but also honors the resilience and traditions of those who have thrived in its embrace.