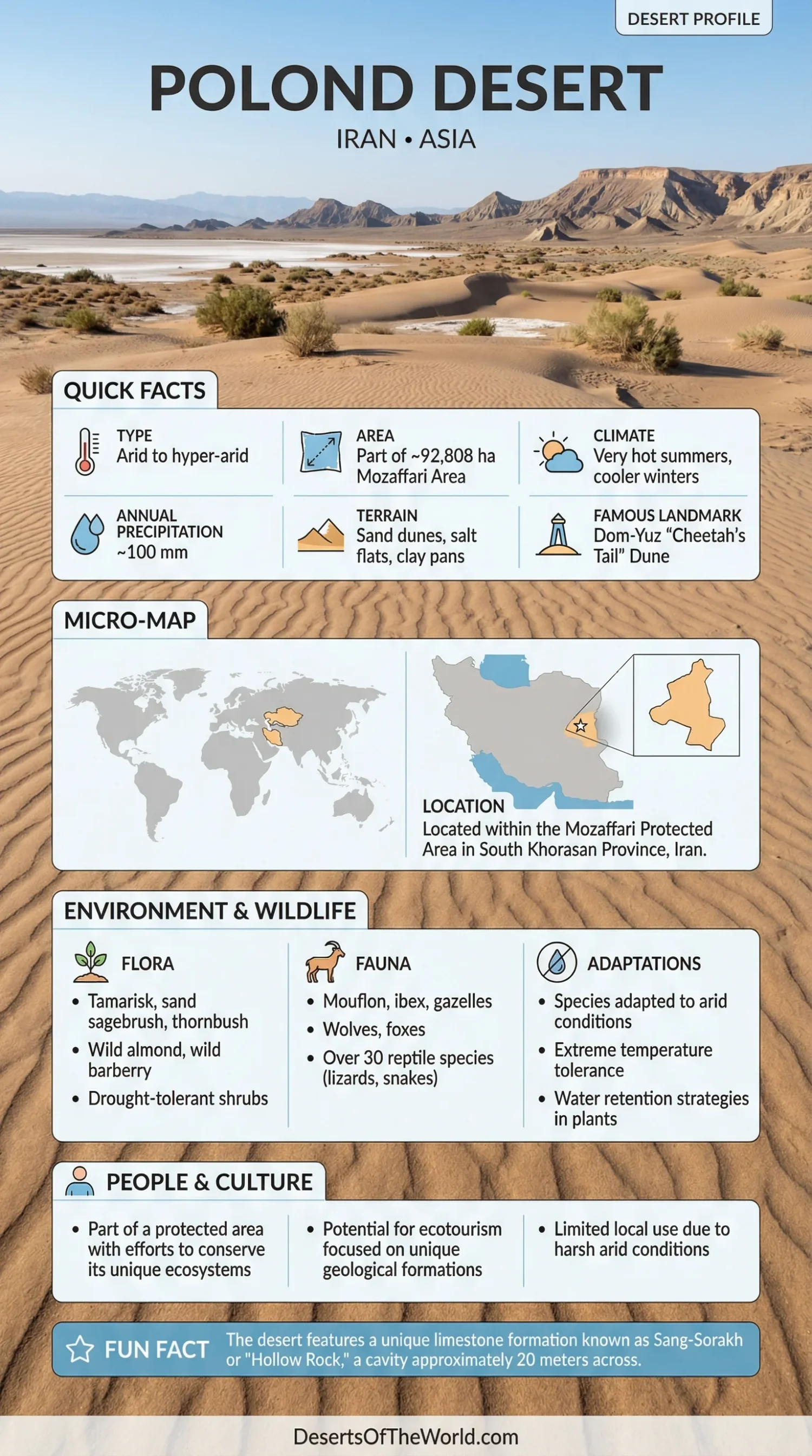
Location & Continent
Continent: Asia
Countries: Iran (South Khorasan Province – within Mozaffari Protected Area)
Coordinates: ~34.16°N, 57.70°E
Click to load the interactive map
Physical Features
Area: Part of the Mozaffari Protected Area (~92,808 ha)
Landscape: Sand dunes, sandy hills, salt flats, clay pans, with adjacent mountainous terrain
Elevation: Desert plains at ~1,000 m, rising toward nearby highlands
Climate & Precipitation
Temperature: Very hot summers, cooler winter nights typical of the Iranian Plateau deserts
Precipitation: Arid to hyper-arid; low annual rainfall with occasional flash floods after storms
Ecological Features
Ecozone: Palearctic (Iranian Plateau)
Biome: Deserts and xeric shrublands
Ecoregions: Mountain–desert mosaic; interface between highlands and desert plains
Flora & Fauna
Flora: Tamarisk, sand sagebrush, locust, thornbush, wild almond, wild barberry, and drought-tolerant shrubs
Fauna: Mouflon, ibex, gazelles, wolves, foxes, and over 30 reptile species (including lizards and snakes)
Geology & Notable Features
Geology: Aeolian sand dunes, clay pans, salt crusts, and eroded limestone formations
Notable Features: Dom-Yuz dune (“Cheetah’s Tail”); Sang-Sorakh (“Hollow Rock”) – a limestone cavity ~20 m across
References
Polond Desert – Wikipedia
Mozaffari Protected Area – Wikipedia
Iran Daily – Enchanting Polond Desert
Iran Daily (PDF) – Flora, fauna, Dom Yuz dune, Sang Sorakh
Introduction to the Polond Desert
The Polond Desert is a lesser-known desert region with varied physical and ecological features. Located in a distinct geographic setting, it supports ecosystems adapted to dry conditions and includes a range of plant and animal species. This section outlines its geography, climate, and biodiversity.
Geography of the Polond Desert
Covering an area of approximately 50,000 square kilometers, the Polond Desert is characterized by its arid landscapes and unique geological formations. Located at approximately 34.16°N latitude and 57.70°E longitude, the desert experiences extreme temperature variations. The terrain includes sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and dry riverbeds, contributing to its diverse geography.
Climate Conditions
Polond Desert exhibits a hyper-arid climate, with annual precipitation averaging less than 100 millimeters. During the day, temperatures can soar up to 50°C, while nights can drop to a chilling 0°C. The seasonal changes are minimal, adding to the harsh survival conditions of its inhabitants.
Seasonal Weather Patterns
The climate of the Polond Desert can be summarized as follows:
| Season | Temperature Range (°C) | Average Precipitation (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Winter | 0 – 20 | 5 |
| Spring | 15 – 35 | 10 |
| Summer | 30 – 50 | 2 |
| Autumn | 15 – 30 | 15 |
Flora and Fauna of the Polond Desert
The harsh conditions of the Polond Desert have led to the evolution of several resilient species. A diverse range of plants and animals have adapted to survive in this arid environment, making the desert a unique ecosystem.
Vegetation
The vegetation in Polond is primarily made up of drought-resistant plants such as:
- Cacti – Notable for their water retention abilities.
- Succulent Shrubs – Adapted to the extreme temperatures.
- Desert Grasses – Limited growth but critical for preventing soil erosion.
Wildlife
Wildlife is sparse but unique, featuring species such as:
- Fennec Foxes – Known for their large ears and nocturnal habits.
- Sand Vipers – Well adapted for camouflage and an important predator in the desert ecosystem.
- Desert Antelopes – Adapted to survive with very little water.
Challenges and Conservation
Despite its seemingly inhospitable conditions, the Polond Desert is facing several environmental challenges. Desertification, human encroachment, and climate change are threatening its delicate ecosystems.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts are being made to conserve the rare species and habitats found in the Polond Desert. Initiatives include:
- Protected Areas – Establishing restrictions on land use.
- Research Programs – Monitoring the health of desert ecosystems.
- Community Engagement – Educating locals about sustainable practices.
Conclusion
The Polond Desert, while less known compared to its counterparts, holds a treasure trove of natural wonders and biodiversity. Its unique climate, geographical features, and resilient flora and fauna make it an intriguing subject for study and conservation. By increasing awareness of the environmental challenges it faces, efforts can be directed toward preserving this remarkable ecosystem for future generations.