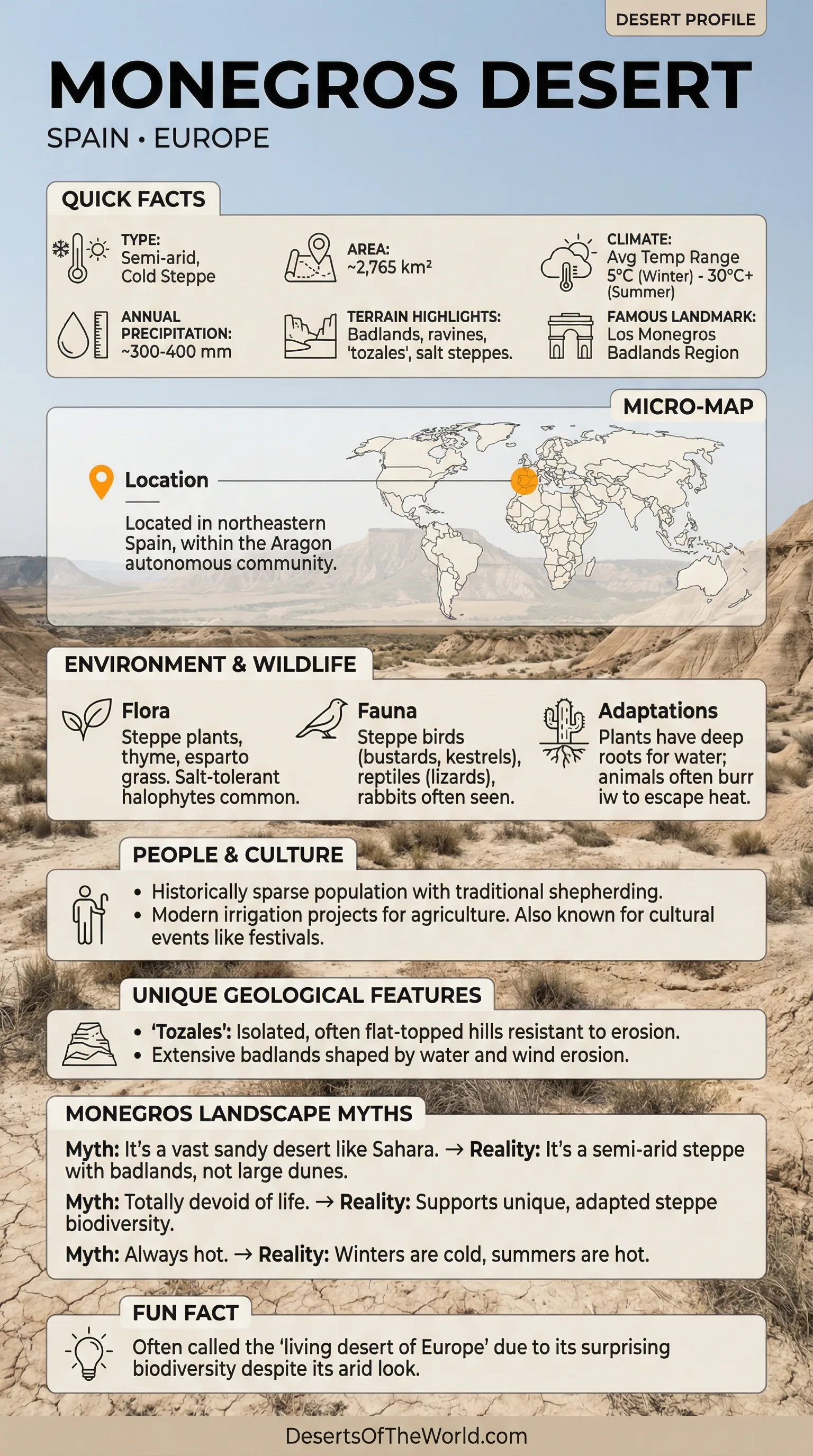
Location & Continent
Continent: Europe
Country: Spain (Aragón region, between Zaragoza and Huesca provinces)
Coordinates: 41°30′N, 0°15′W
Click to load the interactive map
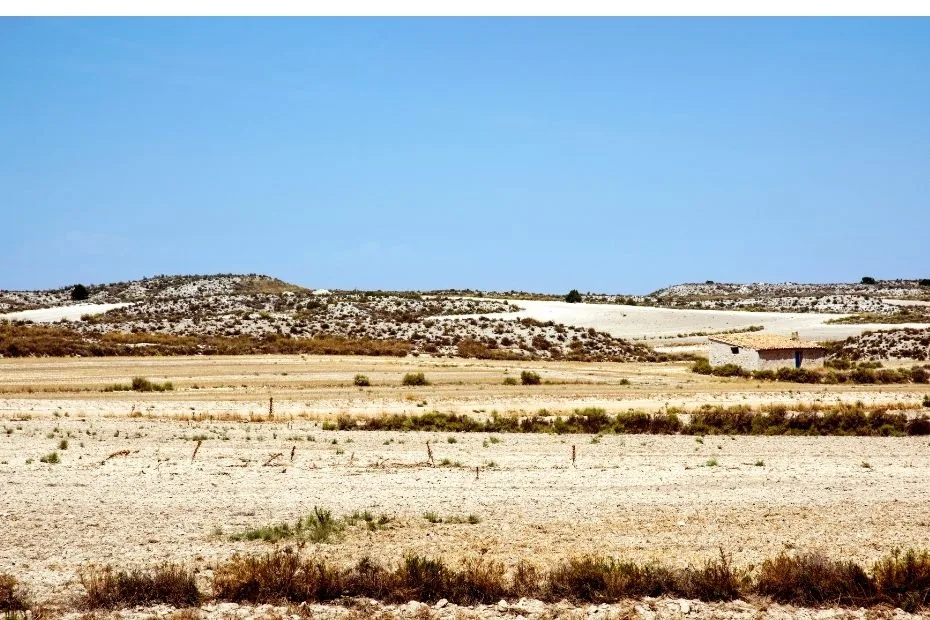
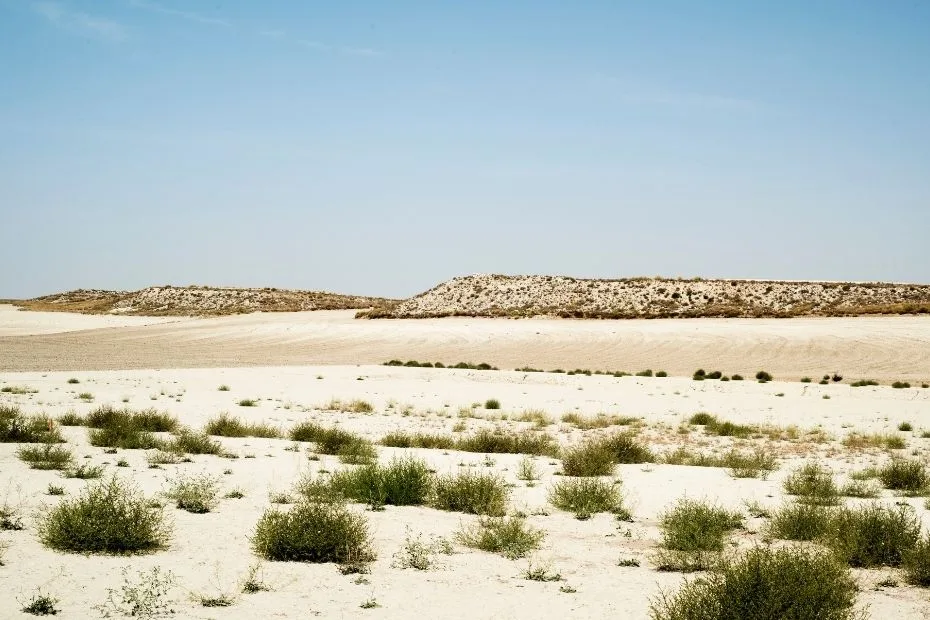
Photos of the Monegros Desert
Physical Features
Area: Approximately 276,440 hectares (2,764 km²)
Length: About 40–50 km
Width: 30–40 km
Elevation: Ranges from 200 m to 500 m above sea level
Climate & Precipitation
Temperature: Hot, dry summers reaching up to 40°C; cold winters dropping below 0°C
Precipitation: Annual rainfall 350–400 mm, very irregular, mostly in spring and autumn
Ecological Features
Ecozone: Semi-arid Mediterranean steppe
Biome: Xeric shrubland and steppe
Ecoregions: Ebro Valley semi-arid habitats
Flora & Fauna
Flora: Shrubs (sagebrush, thyme, rosemary), esparto grass, adapted salt-resistant plants
Fauna: Dupont’s lark (rare bird), great bustard, little bustard, European rabbit, reptiles, and several endangered invertebrates
Geology & Notable Features
Geology: Semi-arid basin formed by sedimentary rocks, gypsum, clay, and saline soils shaped by erosion
Notable Features: Bardenas-like badlands, gypsum hills, salt flats, and steppe plains
Monegros Desert Festival
Overview: The Monegros Desert Festival is one of Europe’s largest electronic music festivals, held annually in the Los Monegros Desert, Aragón, Spain. It gathers tens of thousands of people from all over the world.
Founded: 1994
Genre: Primarily electronic music (techno, house, drum & bass, hip hop)
Attendance: Around 50,000–70,000 visitors each year
Duration: 24-hour non-stop event
Highlights: World-class DJs, massive stages set in the desert landscape, unique fusion of music and art installations
Introduction
The Monegros Desert, located in northeastern Spain, is a semi-arid region known for its dry terrain and varied plant and animal life. Although the climate is harsh, many species have adapted to survive in these conditions. This section examines the geography, climate, and key characteristics of the Monegros Desert, as well as its ecological and cultural role.
Geography
The Monegros Desert spans approximately 2,700 square kilometers in the province of Huesca, within the autonomous community of Aragon. The region is characterized by flat plains, rolling hills, and a few rugged formations, forming a striking contrast against the surrounding fertile landscapes.
Landforms and Soil
The soil in Monegros is primarily composed of clay, sand, and gravel, providing limited fertility. This factor, combined with minimal vegetation, contributes to its semi-desert classification. The Monegros Mountain Range to the northwest adds a scenic backdrop, with peaks that rise steeply from the arid plains.
Water Sources
Water is a scarce resource in the Monegros Desert, with the primary water source being the Guatizalema River. Despite its limited availability, several small irrigation channels can be found, supporting agriculture in certain areas where crops like olives and almonds are grown.
Climate
The climate in the Monegros Desert is classified as a semi-arid Mediterranean climate, characterized by dry summers and mild winters. Average annual precipitation is around 300mm, mostly occurring in spring and autumn.
Temperature Extremes
The Monegros shows wide seasonal temperature differences. Summer temperatures can reach 40°C (104°F), while winter temperatures may fall to -5°C (23°F). These extremes shape the region’s plant and animal communities.
Biodiversity
Despite its arid conditions, the Monegros Desert harbors a surprising array of flora and fauna. The vegetation mainly consists of xerophytic species, adapted to survive with minimal water.
Flora
- Shrubs: Various species like Thyme and Rosemary.
- Grasses: Includes drought-resistant grasses suitable for grazing.
- Trees: Sparse populations of Pine and Juniper.
Fauna
The animal life is equally fascinating, with species such as the Spanish ibex, eagles, and various reptiles thriving here. The Monegros Grassland is particularly notable for its population of steppe birds, including the endangered Little Bustard.
Cultural Significance
The Monegros Desert has been shaped by human activity for centuries. Traditional agricultural practices, combined with modern interpretations of land use, have led to a unique cultural landscape.
Local Communities
Scattered throughout the desert are small villages where residents engage in agriculture and animal husbandry. Distinct traditions and cultural practices have developed, reflecting the resilience of the local people.
Tourism
The increasing interest in ecotourism has sparked awareness about the Monegros Desert’s incredible natural beauty. Activities like hiking, bird watching, and photography attract visitors who seek to experience the unique landscapes and wildlife.
Conclusion
The Monegros Desert is shaped by harsh environmental conditions that have influenced both its ecosystems and local communities. Its landscapes, biodiversity, and history reflect the long relationship between people and the natural environment. As global environmental pressures increase, protecting the Monegros Desert helps conserve its wildlife and preserve the cultural heritage of those who live there.
Key Features of Monegros Desert
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Area | 2,700 km² |
| Climate | Semi-arid Mediterranean |
| Annual Rainfall | 300mm |
| Temperature Range | -5°C to 40°C |
| Notable Species | Spanish ibex, Little Bustard |